 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 9-258
the normal. See angle of reflection. Regular reflection
objects or points close together. No lens or optical
system can form a perfect image of a point; it will appear
as a small disk surrounded by concentric circles. If two
occurs when the surface is irregular and the reflected
points are so close together that the disks overlap, the
light diverges from each point as if it were a separate
points cannot be distinguished separately; they are not
reflecting surface. Diffused rays are scattered, go in
resolved. The measure of the resolving power is the
many directions, and will not form a distinct image.
Refracted ray - The ray of light passing through and
angle subtended at the optical center of the lens by two
points which are just far enough apart to permit
leaving a refracting surface representing the path of light
resolution into two separate images. This angle is
after refraction (fig 2-24).
termed the limiting angle of resolution.
Refracting power - The power of a lens or lens
Retaining ring - A thin ring threaded on the outside
system to converge or diverge light. See diopter.
Refraction - The bending of light which occurs when
surface. It is screwed into a tube, cell, or other body
member of an optical instrument to retain or hold a lens
a ray of light passes obliquely from one medium to
or other part in fixed position.
another of different optical density.
See angle of
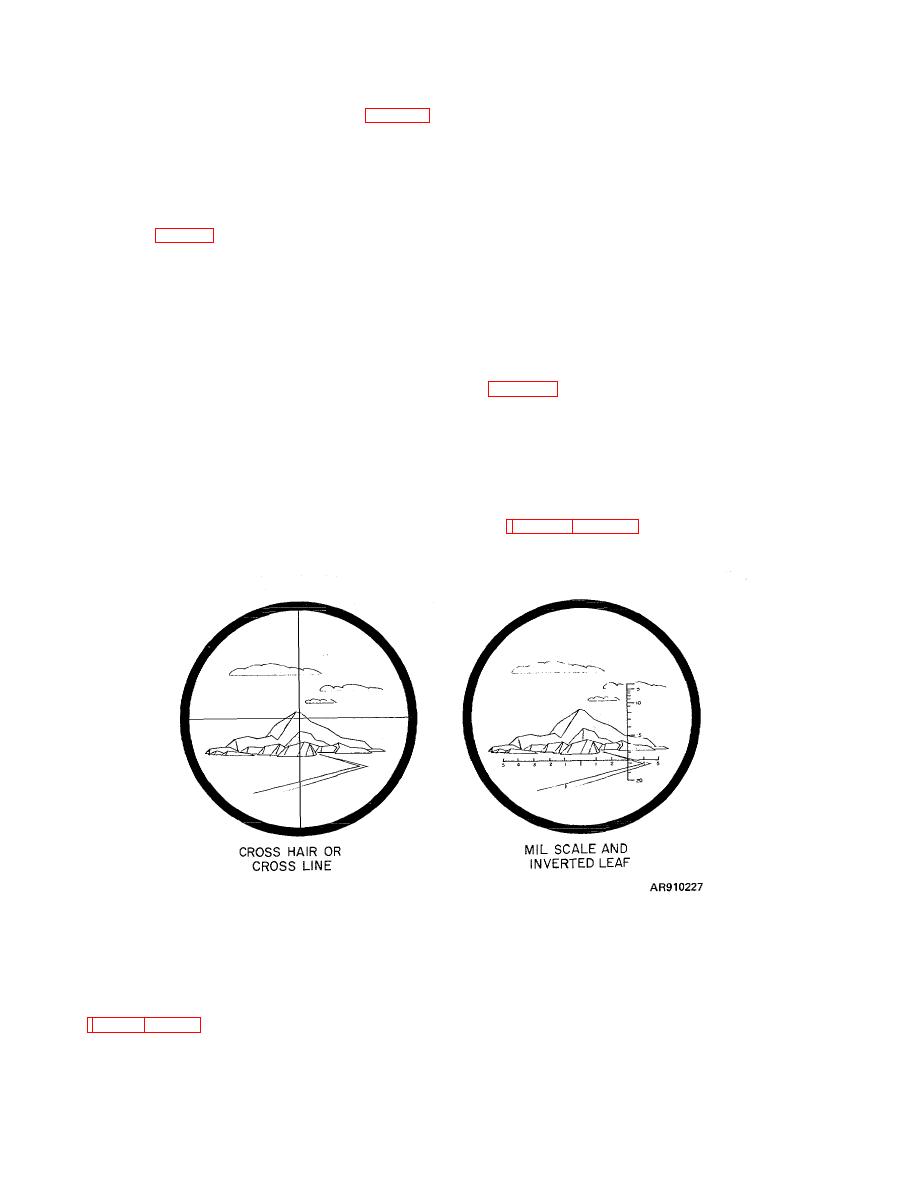
Reticle - Marks or patterns placed in the focal plane
refraction and angle of deviation.
Refractive index - See index of refraction.
of the objective of an optical instrument which appear to
the observer to be superimposed upon the field of view
Regular reflection - See reflection.
Relief - Effect of stereoscopic or three dimensional
sighting or aiming; to measure angular distance between
vision; solidity or depth; sharpness of outline due to
two points; to determine the center of the field; or to
contrast of the object standing out, from a background.
assist in the gaging of distance, determining leads, or
Resolution - In optics, the ability of a lens system to
measurement. The reticle may be a pair of crosslines
reproduce an image in its true sense. Forming separate
composed of fine wire or may be etched on a glass plate
images of two objects or points very close together.
with plane parallel surfaces. If it is etched on glass, the
Resolving power - A measure of the ability of a lens
entire piece of glass is referred to as the reticle. (Also,
or optical system to form separate images of two
see figs 4-24 and 4-25).
Figure B-27. Reticle patterns superimposed on image of object .
Retina - The light-sensitive inner coat or tunic of the
right becomes left and vice versa. It is the effect
produced by a vertical mirror in reflecting an image.
eyeball upon which the image is formed by the lenses of
Reverted erect - See erect image.
the eye. It contains the visual cells called the cones and
Reverted image - An image, the right side of which
Reversion - Turned the opposite way so that
appears to be the left side of the object and vice versa.
B-27
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |