 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 9-258
Reverted inverted - See inverted image.
the line of sight to a limited degree. See correction
Rhomboidal prism - A prism with two pairs of parallel
wedge, measuring wedge.
sides forming right angles and two 45ƒ slanting or
Rouge - A material for polishing optical glass made
principally from red oxide of iron. The name is also
oblique parallel ends. It will displace the path of light
applied to polishing materials which are not red, such as
entering its ends without changing the direction of light.
black rouge and white rouge.
It does not invert or revert the image (fig 4-12).
Sclera - The outer of the three coats or tunics of the
Rhomboidal prisms may be rotated to divert the lines of
eyeball. It is tough, white, and flexible and is the white
sight to permit interpupillary adjustment of the eyepieces
portion of the eye normally seen. The slightly protruding
of a binocular instrument.
transparent portion of the center front of the eye, the
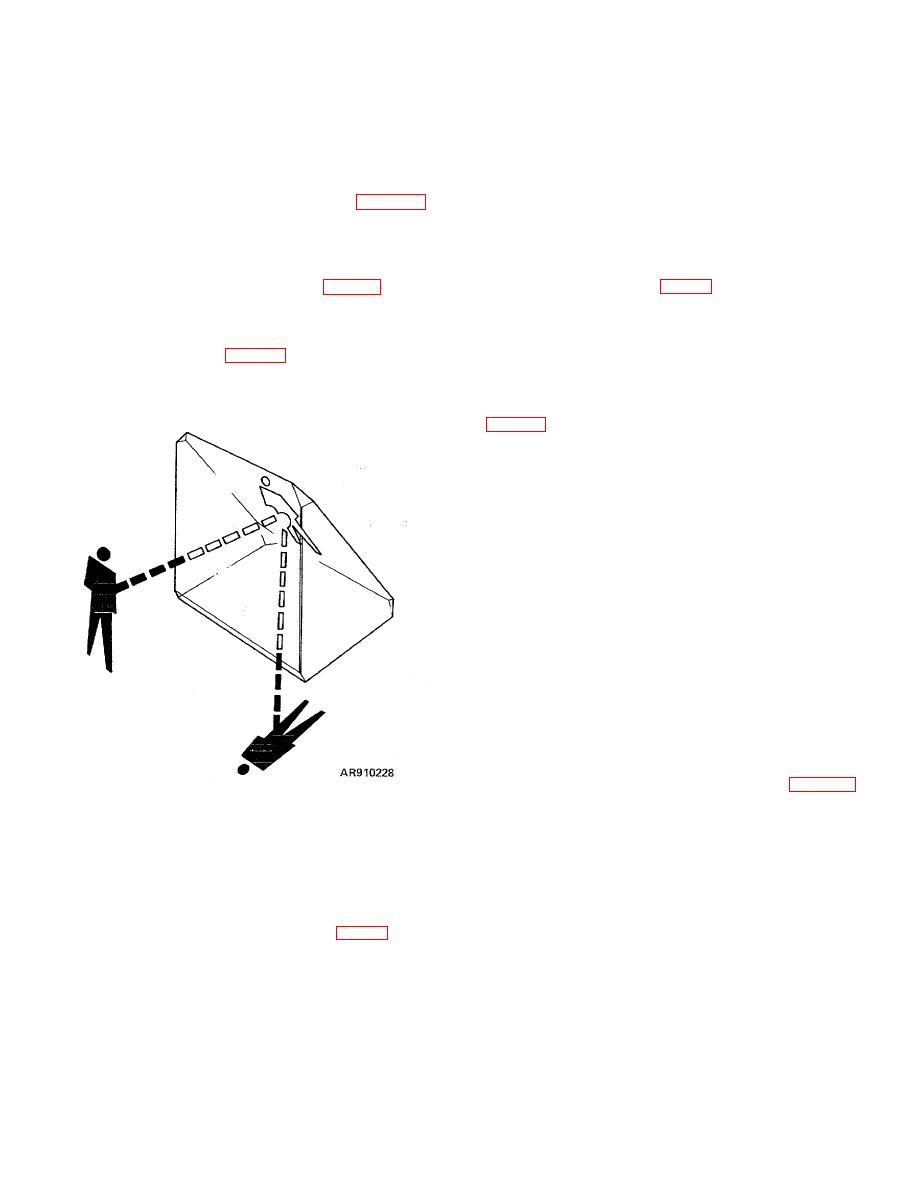
Right-angle prism - A type of prism used to turn a
cornea, is part of this coat (fig 3-2).
beam of light through a right angle (900) (fig 2-36). It will
Second - A unit of measurement of an angle equal to
invert (turn upside down) or revert (turn right or left),
one-sixtieth of a minute or 1/3600th part of a degree.
according to position of the prism, any light reflected by
Selective absorption - See absorption.
it. This prism is likewise used to turn a beam of light
through an angle of 180ƒ (fig 2-43) when either a normal
Selective reflection - See absorption.
Selective transmission - See absorption.
erect image or inverted, reverted image is produced,
Separator - Also known as spacer. A hollow tubular
depending upon the position of the prism with respect to
part used to separate two lenses at a definite distance
the object and the observer.
Sighting instruments - Devices or instruments
designed to aid in the pointing of a weapon, observation
and azimuth or range determination, and looking over
Sine - The sine of an angle is the side of a right-
angle triangle opposite the angle divided by the
hypotenuse (the long side opposite the right angle).
Site Location - See angle of site.
Soft coat - A term designating the soft coating
applied to coated optics to differentiate between the
harder and more durable coating of magnesium fluoride
known as hard coat.
Spacer- See separator.
Spectrum - The band of colors produced by a prism
in dividing white light into its components.
The rainbow is an example, dispersion produces this
spectrum. See electromagnetic spectrum.
Spherical aberration - The aberration of a lens which
results when rays of light which pass through a lens near
its edge are converged to a point nearer the lens than
those rays passing through near the center (fig. 2-55).
Figure B-28. Right-angle prism .
The effect is poor definition of the image.
Split field - The field of view as seen when observing
Rod - One of the two types of light-sensitive
through a coincidence range finder. It is formed by
elements or visual cells in the retina of the eye which
uniting halves of the images produced by two objectives.
permit sight. The rods are associated with night vision
The half images are separated by the halving line.
and sight under other conditions of weak light. They also
Squint - See strabismus.
detect motion. For seeing in weak light, they are
Stadia scale - Graduations on a reticle which in
stimulated by a substance known as visual purple. The
conjuction with a rod of definite length can be used to
other type of visual cell is termed the cone (fig 3-5).
measure distances.
Roof-angle prism or roof prism - See Amici prism.
Standard candle - Initially a sperm whale oil candle,
Rotating prism - See Dove prism and Pechan prism.
7/8 inch in diameter, burning at the rate of 120 grains per
Rotating wedge - A circular optical wedge mounted
hour. Current standards of candle power are electric
to be rotated in the path of light to divert
lamps.
B-28
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |