 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 9-258
CHAPTER 6
PRINCIPLES OF LASERS
from the partially mirrored end of the tube.
6-1.
General.
Simply defined, a laser (Light
(4) Liquid-type lasers consist of solutions
Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) is a
such as coumarine and rhodamine red. In this type of
light-emitting body with feedback for amplifying the
laser, the liquid-laser materials are stimulated to
emitted light.
The laser is a unique, and highly
emission by irradiating the lasing liquid or dye solution
specialized source of light; the beam of light it produces
with another laser beam.
has three significant characteristics, namely, laser light is
b. Although the heart of a laser is a light wave
monochromatic, highly collimated, and coherent.
amplifier, the device produces a beam when it oscillates.
Although light possessing the first two properties can be
The laser is, therefore, a special kind of oscillator, but it
produced by some conventional light sources, only laser
will optically behave in the same manner as ordinary
light possesses all three properties. In addition, the laser
light. For this reason, only gas lasers and solid-state
beam is a powerful and very intense light source.
rod-type lasers, are described in detail.
6-2.
Types of Lasers.
6-3.
Gas Lasers.
a. There are essentially four types of lasers:
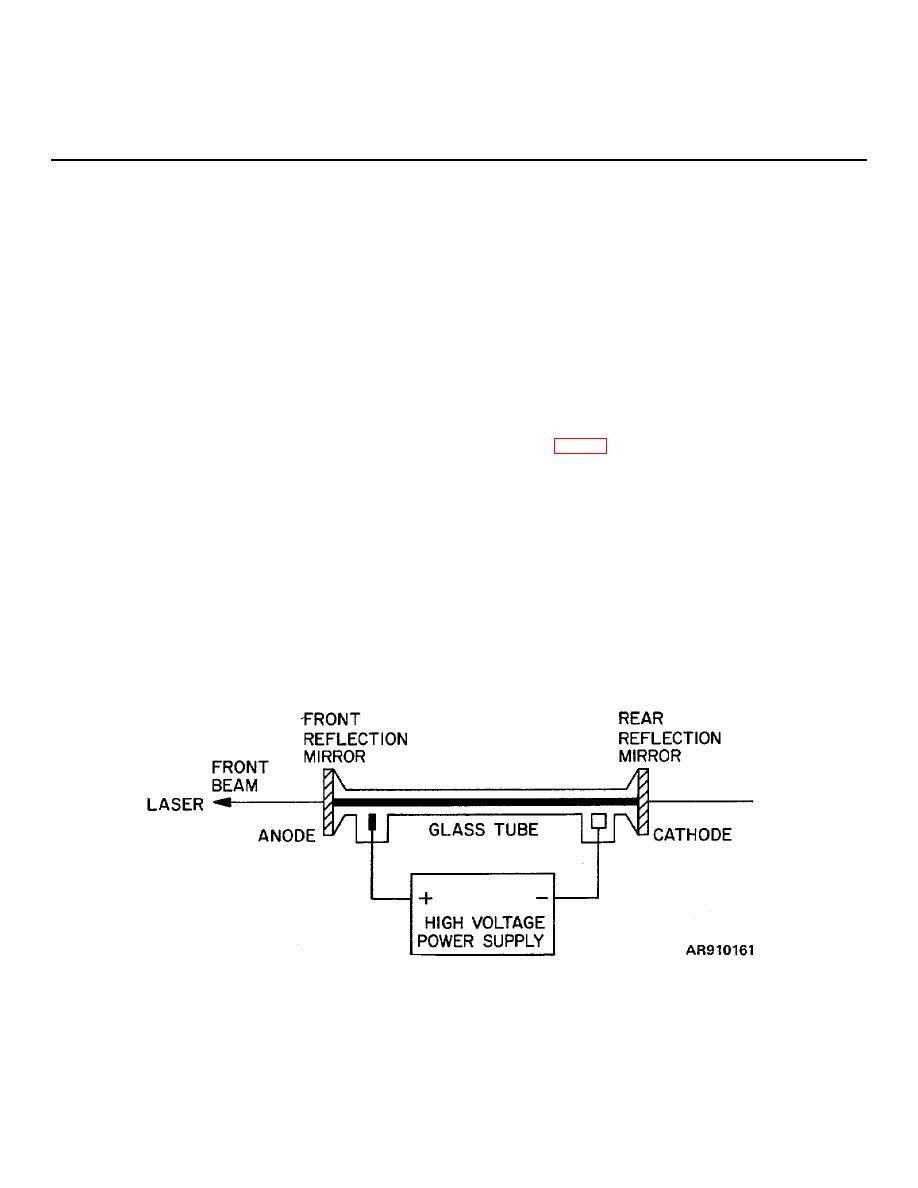
a. A gas laser is structurally a simple device,
(1) Solid state rod-type lasers use
and in many ways it is similar to neon electric signs. A
materials such as a ruby rod of about 1 centimeter in
gas laser (fig 6-1) consists of a thin glass tube about 1
diameter and 15 centimeters long as an elementary light
foot long, and filled with a low-pressure mixture of helium
emitter or generator.
and neon gases. A pair of electrodes, a negative
(2) Semiconductor
diode-type
lasers
cathode and a positive anode, are mounted near the
use material such as gallium arsenide and consist of a
ends of the tube. These electrodes are connected to a
junction formed by p-type material and an n-type
high voltage, direct current power supply. The electric
material. In this type of laser, stimulation to laser
field produced between the two electrodes breaks down
emission occurs by passing a current through the
the column of gas, instantly transforming it from a poor
junction.
conductor of electricity into a relatively good conductor.
(3) Gas-type lasers use helium-neon,
A continuous electric glow discharge takes place within
argon, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and Xenon. In this type
the glass tube, and produces a continuous electric
of laser, stimulation to laser emission occurs by passing
current flow between cathode and anode through the
a current through the gas. The current causes the gas to
partially ionized column of gas.
ionize and radiate. The radiation oscillates within a tube
provided with mirrored ends and then discharges
Figure 6-1. Gas laser.
6-1
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |