 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
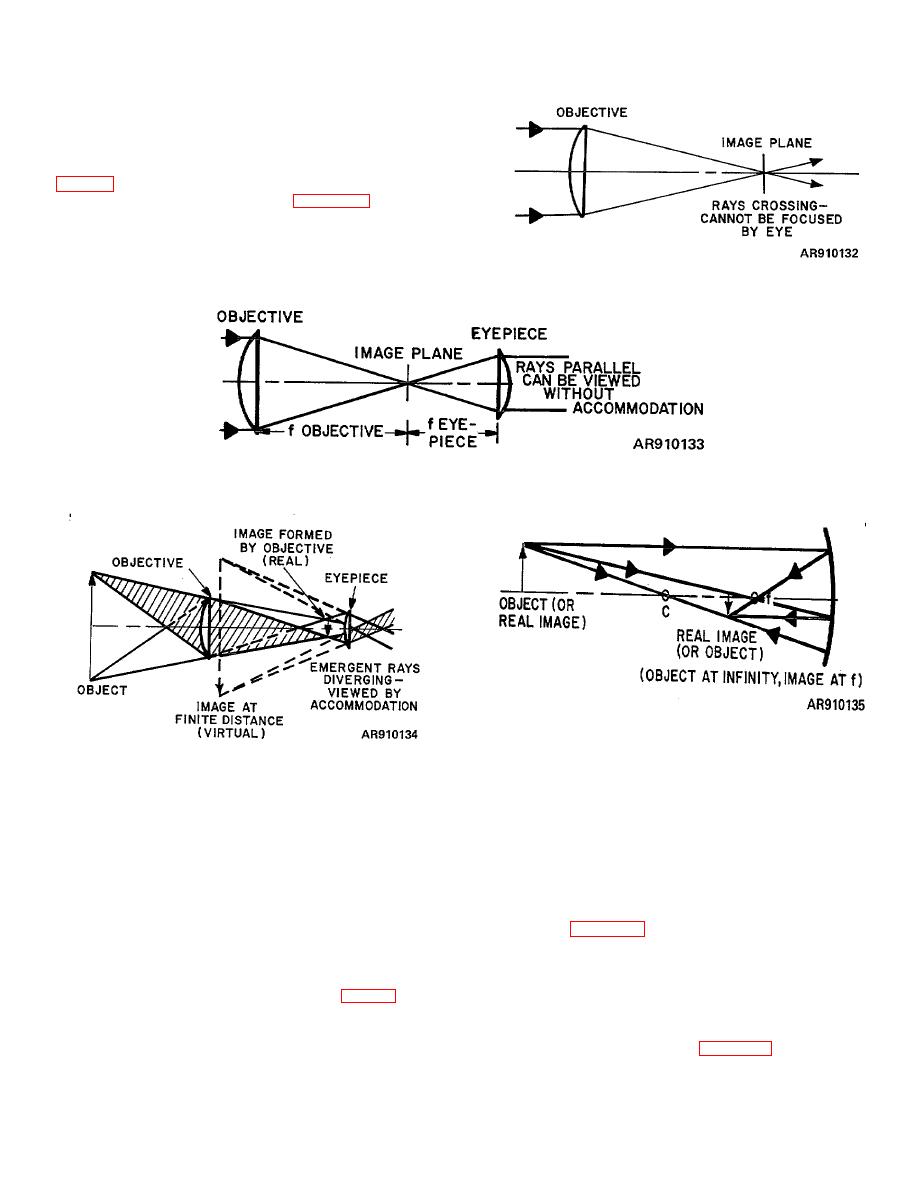 TM 9-258
eye. However, if another positive lens is placed between
such an image and the eye, and the real image lies at
the first focal point of this eyelens, the eye can see
without accommodation of a virtual image of the object
seen by the objective lens. This is the Keplerian system
simplest form and is illustrated in figure 5-6 with the
virtual image moved in to the near point of the eye. This
system generally is limited to astronomical observation
becasue the image is inverted. The Army uses this
system only to adjust other types of telescopes and when
it is so used, calls it a collimating telescope.
Figure 5-4. Objective lens.
Figure 5-5. Keplerian system
Figure 5-7. Concave mirror
Figure 5-6. Refracting astronomical telescope
(a) An object beyond center of
curvature forms a real image between center of
5-6.
Reflecting Telescopes.
curvature and focal point. This image is smaller than the
a. Types of Spherical Mirrors.
object and inverted and reverted.
(1) Convex. In this case, the mirror surface is
(b) When the object is between the
on the outside of a spherical surface, the center of
center of curvature and the focal point, the image is
curvature of which lies on the side opposite the incident
formed beyond the center of curvature and is real,
light. This type of spherical mirror produces small virtual
enlarged, and inverted and reverted.
image only. It is frequently used on trucks as a rearview
b. Reflecting Telescope.
This telescope,
mirror.
diagramed in figure 5-8, utilizes a concave mirror of long
(2) Concave. In this type, the light is incident
focal length (instead of an objective lens) to form the real
on the same side as the center of curvature (C) of the
image. This is viewed as a virtual image through an
sphere. The focal point (f) is located halfway between
eyepiece which magnified it or is photographed by a
center of curvature and reflecting surface (fig 5-7). The
camera attachment. The Mt. Palomar telescope, for
concave mirror forms virtual and enlarged images of
example, has a 200-inch diameter mirror of long focal
objects within its focal length which is one-half the radius
length, great light-gathering ability, and great resolving
of curvature. Some of the uses to which it is put are
power. (For resolving power see para 5-30).
headlamp reflectors, searchlight reflectors, and objective
glasses in astronomical telescopes.
5-3
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |