 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Figure 4-2. Comparative focal lengths of elements in compound lens. |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
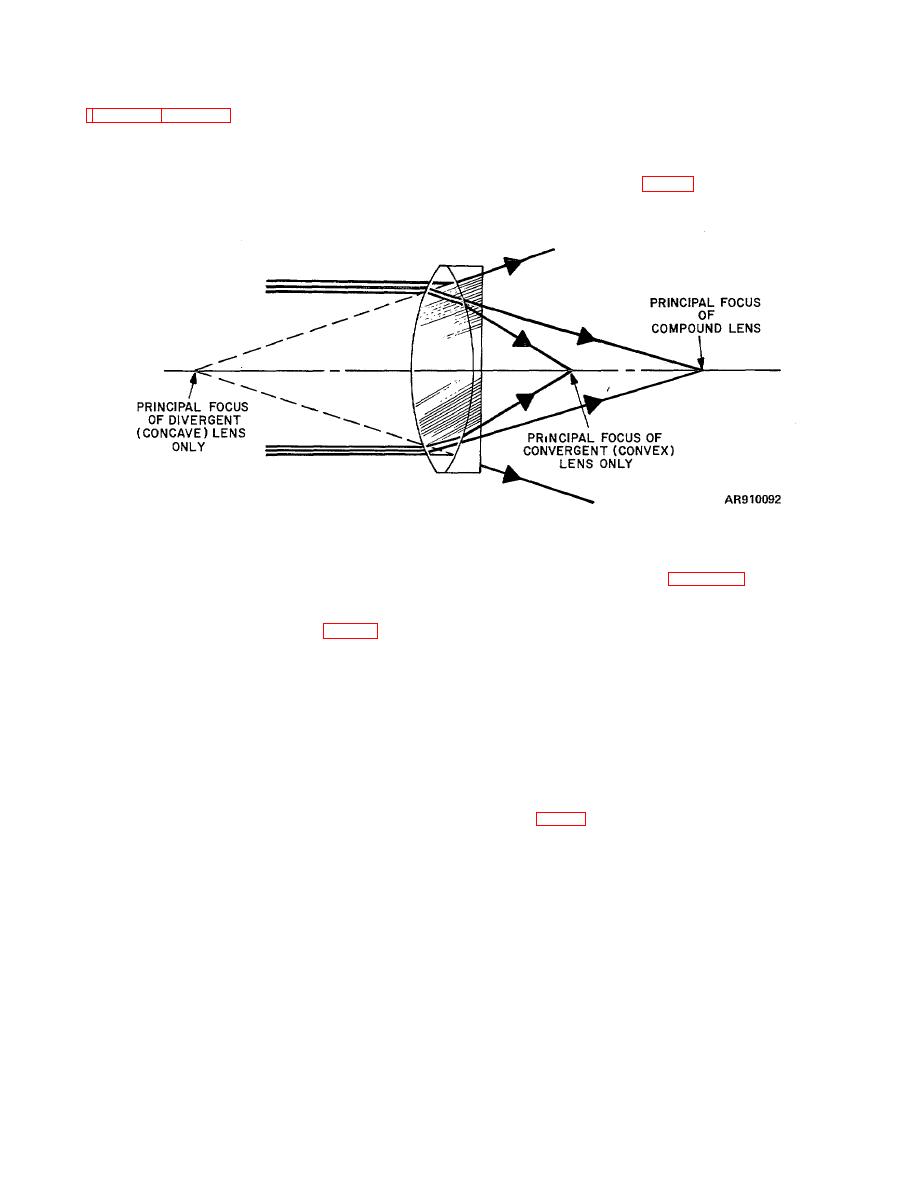 TM 9-258
aberrations or defects which are present in the single
refraction power of the former but sufficient dispersive
lens (paras 2-37 thru 2-42).
power to neutralize the dispersion. The result would be
(1) The refractive power of a compound lens is
that light passing through this compound lens would be
less than that of the convex lens alone. For example, if a
brought to a practical focus at a point that would be
double-convex lens of crown glass is combined with a
about double the distance of the point of principal focus
planoconcave lens of flint glass, the latter would have
of the crown lens alone (fig 4-2).
little more than half the
Figure 4-2. Comparative focal lengths of elements in compound lens.
(2) The elements are frequently cemented
at the two surfaces in contact, if the cement used, such
together with their optical axes in alinement. Two lenses
as thermosetting cement (para 2-12c), is a substance
may be cemented together as a doublet or three may be
having approximately the same index of refraction as
cemented together as a triplet, or each lens of the unit
glass.
dialyte compound lens, the inner surfaces of the
4-3.
Objectives.
a. General. The lens nearest the object in any
dissimilar faces of the two lenses cannot be cemented
together inasmuch as they are ground to different
optical system of the refracting type is called the
curvatures in order to correct for aberrations; the two
objective. Its function is to gather as much light as
lenses are separated by a thin ring spacer and are
possible from the object and form a real image of that
secured in a threaded cell or a tube with burnished
object. Objectives lenses in most optical instruments
edges. The cementing of the contact surfaces, ground
form real images (except Galilean telescope).
b. Construction. The majority of objectives are
to the same curvature, generally is considered desirable
because it helps to maintain the two elements in
constructed of two elements, a double-convex
alinement under sharp blows, it aids cleanliness, and it
converging lens of crown glass and a planoconcave flint
decreases the loss of light through reflection
lens (A, fig 4-3).
4-3
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |