 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Figure 4-1. Types of simple lenses. |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
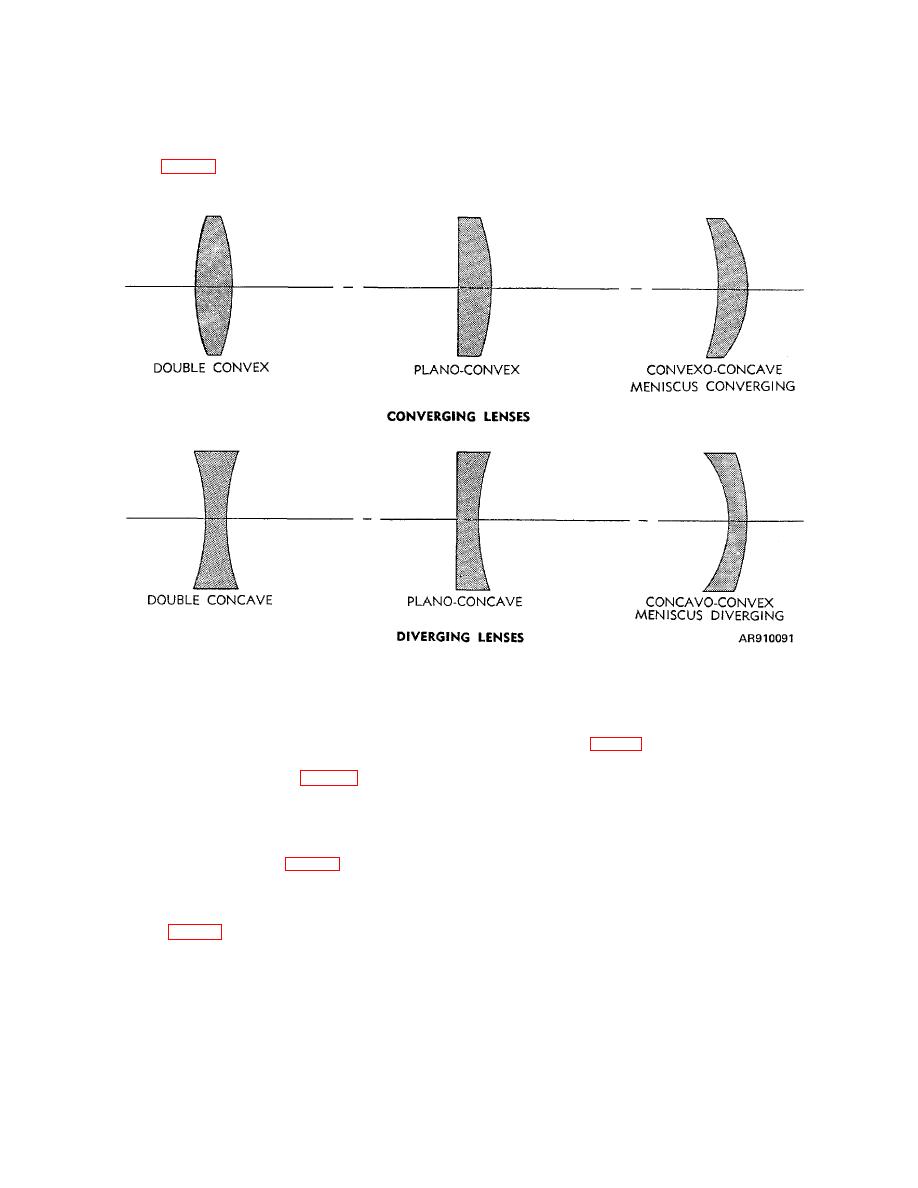 TM 9-258
both spherical. Lenses deceive the eyes by bending rays
class forms real images and lenses in this class are
of light so that, depending on the type of lens, they
termed convex, convergent, positive, or collective lenses.
appear to come from closer and larger objects or from
The other class can form by itself only virtual images and
farther and smaller objects. Lenses are divided into two
lenses in this class are termed concave, divergent,
general classes (fig 4-1). One
negative, or dispersive lenses.
Figure 4-1. Types of simple lenses.
(1) Convex lenses. All convex or converging,
spectacles because they permit undistorted vision
positive lenses are thicker in the center than at the edges
through their margins 'as the eyes are rotated in their
and will converge light from sources and objects. Both
sockers.
(2) Concave Lenses. Concave or diverging,
faces of a convex lens may be convex, one surface may
be convex while the other is flat (termed plano or plane),
negative lenses (fig 4-1) are thinner in the center than at
or one face may convex while the other is concave.
the edges and will diverge light from sources and
(a) A double-convex lens (fig 4-1) is one in
objects. Both surfaces of a divergent lens may have a
which both surfaces have convex curvature. Both
concave curvature (doubleconcave); one surface may be
surfaces contribute to the converging power of the lens.
concave and the other plane (planoconcave); or one face
The greater the convexity of the surfaces, the shorter the
may be concave while the other is convex (concavo-
focal distance.
convex or divergent meniscus), with both centers of
(b) A planoconvex lens (fig 4-1) has a plane
curvature on the same side of lens.
(3) Cylindrical lenses. Cylindrical lenses are
surface and a convex surface. The plane surface does
ground with a cylindrical surface instead of a spherical
not contribute to the converging power of the lens.
(c) The convexo-concave
or, meniscus
one; they are either positive or converging, or else they
are negative or diverging. Their use is very limited. They
are used in some of the coincidence range finders.
concave surface with both centers of curvature on the
b. Compound Lenses. As an optically perfect
same side of lens. The more powerful convex curve
single lens cannot be produced, two, three, or more
makes this a positive lens despite the fact that the
lenses ground from different types of optical glass are
concave surface tends to diverge the light, thus
frequently
combined
as
a
unit
to
cancel
subtracting from the converging power of the lens.
Meniscus
lenses
are
mainly
used
for
4-2
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |