 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 38-400/NAVSUP PUB 572/AFMAN 23-210 MCO 4450.14/DLAM 4145.12
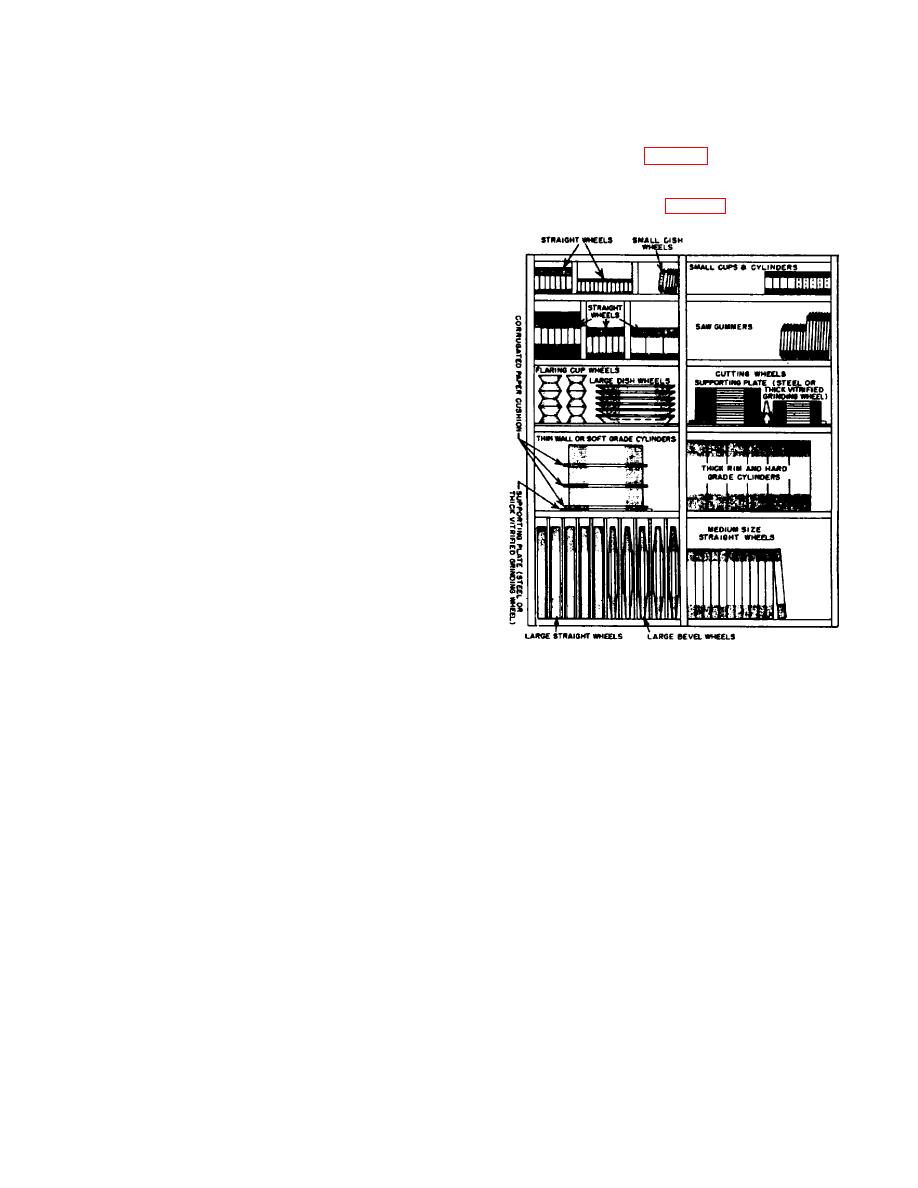
should be built to accommodate wheels of various sizes.
(b) Used serviceable tubes should be
Separate sections of storage racks should be
completely deflated by removing the valve core. They
constructed within standard shelving to prevent the
can be folded and stored.
wheels from rolling off (fig 5-46). Wheels of the same
(c) Tubes will be placed in storage
size, type, and specification should be stored together
grouped according to size and type. Removal from
and should be arranged, so far as possible, to facilitate
storage will be on the basis of oldest stock first.
issue on the basis of FIFO (fig 5-47).
(d) Self-sealing tubes must be inflated
enough to retain full molded size. Storage aids (e.g.,
pallet support sets) will be used to assure retention of
shape and size.
d. Solid rubber tires and track components. Solid
rubber tires, rubber components of combat vehicle
track, track support rollers, and track idler wheels will be
protected as outlined in c above.
e. Rubber cements. Rubber cements must be kept
within 32 . to 90 . and all containers must be kept
F
F
tightly closed at all times. Rubber cements, dependent
upon flash point, are either flammable liquids or
combustible liquids and must be considered for storage
in light of their flammability properties.
5-36.
Abrasive or Grinding Wheels.
a. General. All grinding wheels are fragile and
should be handled and stored carefully to prevent
breakage and chipping.
b. Location. Wheels should be stored in covered,
dry areas, and should not be exposed to extreme
temperature changes. Escaping steam and rain will
seriously affect grinding wheels; consequently, such
Figure 5-46. Bin storage of grinding wheels.
wheels should be away from radiators and open
windows.
c. Storage. Generally, grinding wheels are stored
in bins and racks. Smaller sizes are often carried in bin
drawers. The bins, racks, or drawers
5-84
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |