 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
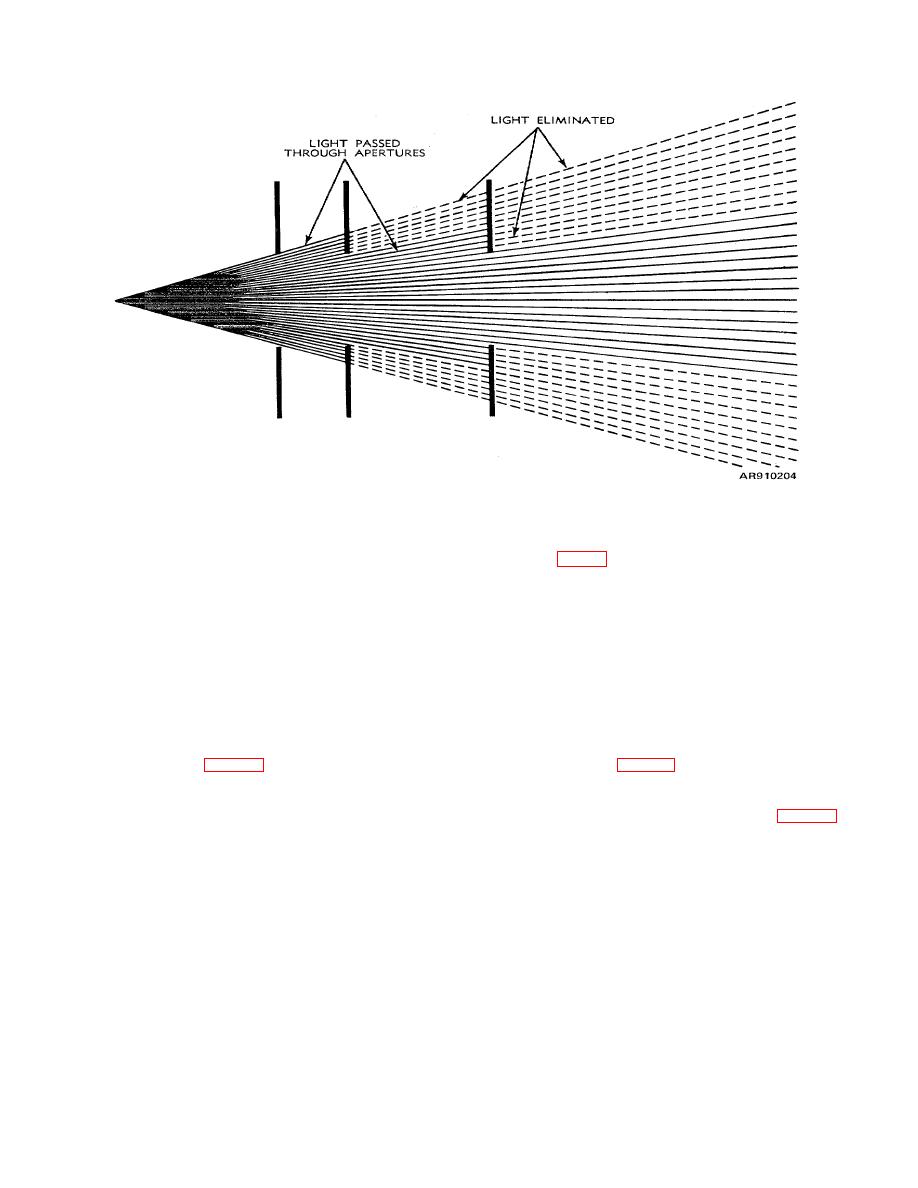 TM 9-258
Figure B-4. Apertures.
Aperture of objective - The diameter of that part of
is contained between the cornea and the crystalline lens
of the eye (fig 3-2).
the objective which is not covered by the mounting.
Arc - A part of the circumference of a circle.
Aperture stop - The diaphragm which limits the size
Artillery - mil See mil.
of the aperture. See diaphragm.
Aplanatic lens - A lens which has been corrected for
Asthenopia - Weakness or rapid fatigue resulting
spherical aberration, coma, and chromatic aberration.
from use of the eyes indicated by headache or pain in
Apochromatic lens - A lens, usually consisting of
the eyes. Often referred to as weak sight or eyestrain.
Astigmatism
three components of different kinds of glass (two crown
a. An aberration or defect of a lens which
glass elements, one flint glass element), which has been
corrected for chromatic aberration with respect to three
causes a point of the object off the axis to be imaged as
selected colors or wavelengths of light.
a short line or pair of short lines. When two lines are
Apparent field of view - The angular size of the field
formed, each is at a different distance from the lens and
of view of an optical instrument, as seen through the
is at an angle to the other, and the lens has two points of
instrument by the eye (fig 2-51). See field of view.
principal focus (B, fig B-5). A sharp image cannot be
Aqueous humor - The transparent liquid which
secured at either focal point and the best results are
obtained at a point between the two focal points in a
B-4
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |