 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
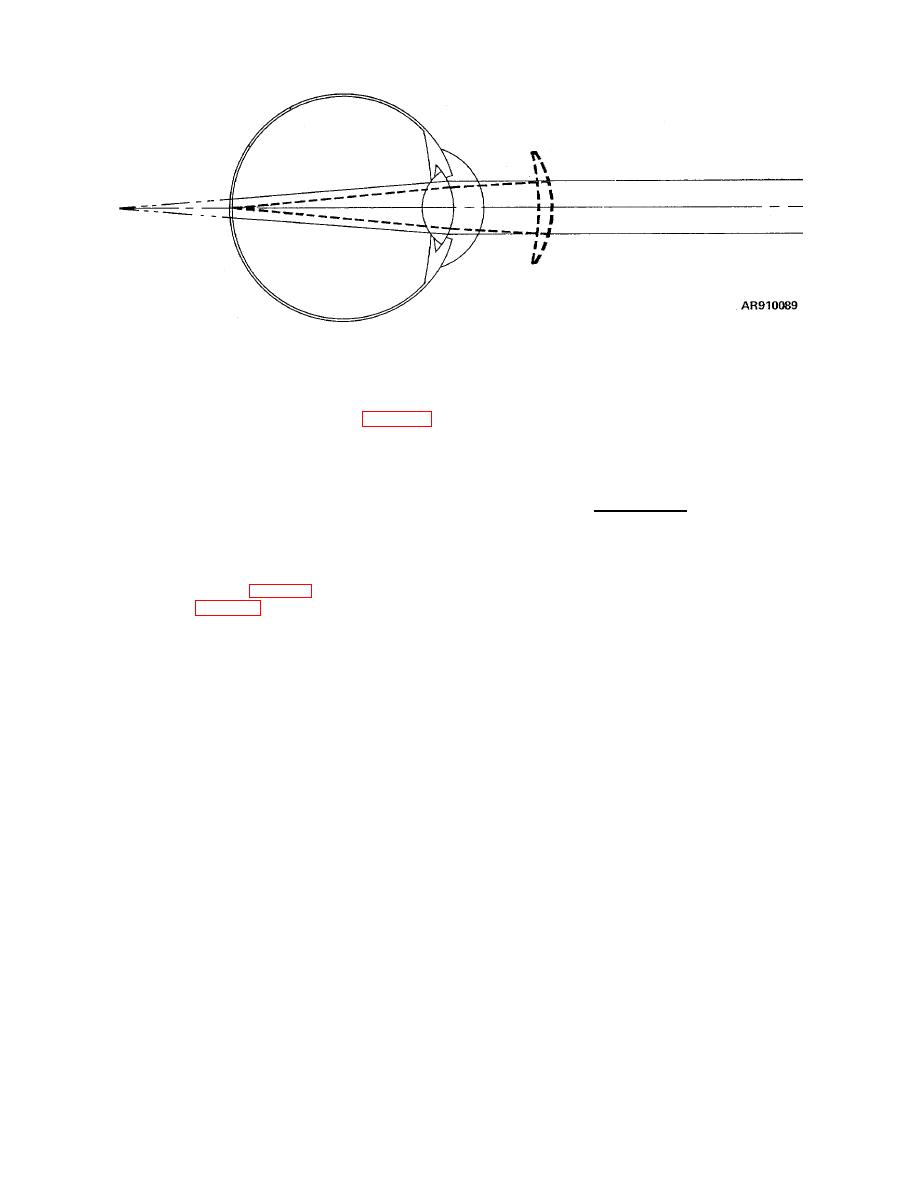
Figure 3-11. Farsightedness (hypermetropia) |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 9-258
Figure 3-11. Farsightedness (hypermetropia)
d. Astigmatism of the Eyes. This condition
observation. This is not to be confused with actual size.
A plane flying away from one will shrink in apparent size
occurs when at least one refracting surface is not
until it is only a speck in the sky. Obviously, it does not
spherical but is somewhat cylindrical (curvature not
become any smaller but, as it recedes, light rays from
symmetrical). In this case the image of a point source is
the wingtips make a progressively smaller angle until the
not a joint image but a short line image as in A, figure B-
eye no longer can separate them and the entire plane
5. Such line images will form from sources on the optical
appears as a single point. Apparent size then is
axis. Thus, visual astigmatism is different from that
inversely proportional to distance and is expressed
encountered in optical instruments (where astigmatism
mathematically as follows:
of a properly centered spherical lens system is zero on
Apparent Size = Size of Object
the axis). This condition is corrected by cylindrical or
Distance to Object
toroidal (toric) spectacles.
When two adjacent objects become so small in apparent
size that any further reduction in size results in failure of
3-11. Visual Limitations.
the eye to separate them, the angle of resolution of the
eye has been reached.
a. Apparent Size (A, fig 3-12). This is the basis
of all magnification (para 2-4 e (1)). It is measured by
the angle the object subtends at the point of
3-15
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |