 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Using the storage space survey worksheet |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 38-400/NAVSUP PUB 572/AFMAN 23-210 MCO 4450.14/DLAM 4145.12
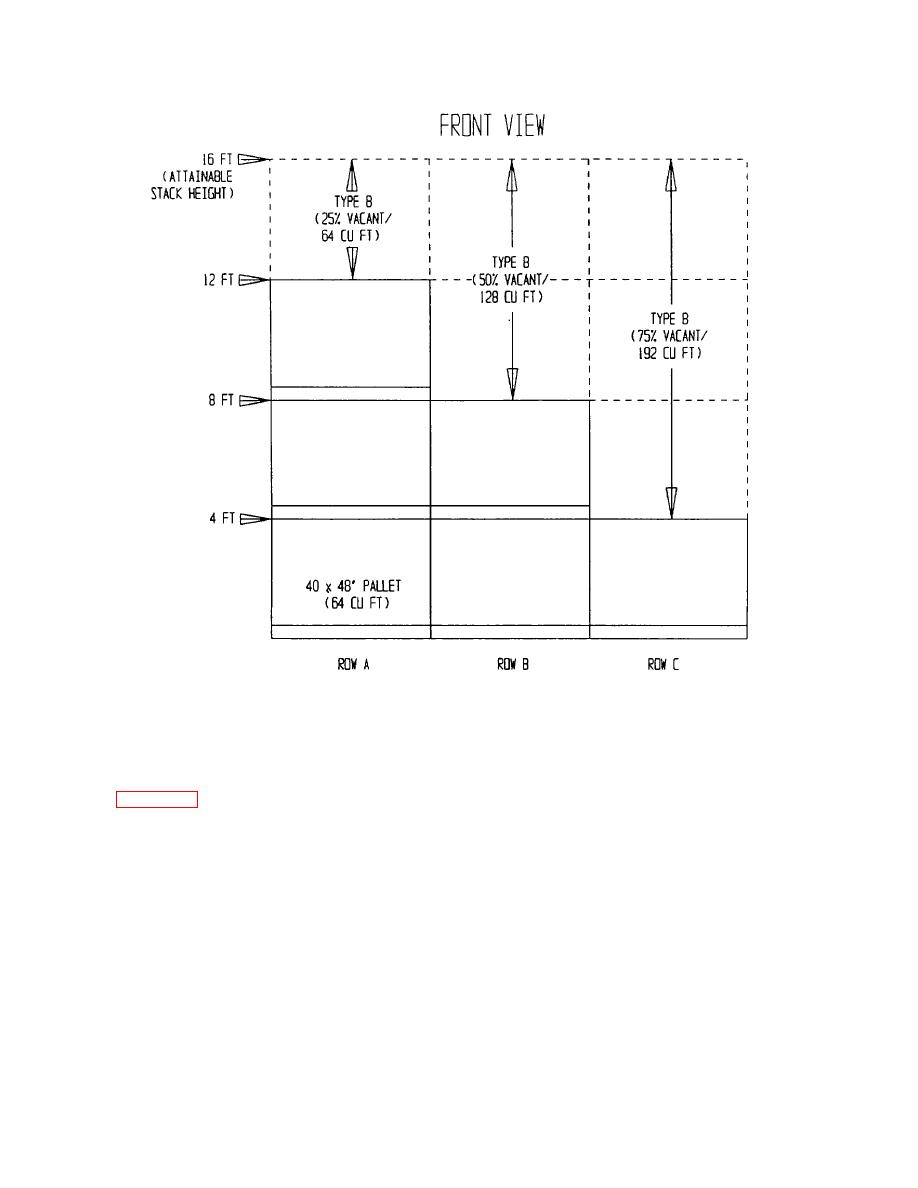
Figure 2-58. Computing Type B Potential Vacant Space
g. Using the storage space survey worksheet. An
(a) Vacant square feet is equal to the
example of using the storage space survey worksheet is
sum of all shaded grids.
shown in figure 2-59. It is completed as follows:
(b) Occupied square feet is equal to the
(1) Shade in area which represent vacant
difference between net square feet and vacant square
space. This includes only space that is actually vacant
feet.
and does not include potential vacant space.
(c) Type A potential vacant space is
(2) Leave unshaded all areas not considered
equal to the sum of all grids annotated "A." (d) Type B
occupied. This includes vacant floor space caused by
potential vacant space is the total cubic feet applied to
short or broken spaces in front of stacks.
the worksheet as calculated by survey personnel.
(3) Label potential vacant space with either
(5) Convert potential vacant space to cubic
an "A" for type A potential vacant floor space (where
feet.
short spaces exist in front of stacks or when
(a) Type A potential vacant cubic space
honeycombing is evident) and with a "B" for type B
is the product of the sum of all grids labeled "A" and the
potential vacant cubic space. This space is marked only
average stack height.
if occupied and recoupable by rewarehousing with
(b) Type B potential vacant cubic space
existing resources (e.g., storage aids, MHE, etc.).
is taken directly from the worksheet.
(4) Summarize the information.
2-60
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |