 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
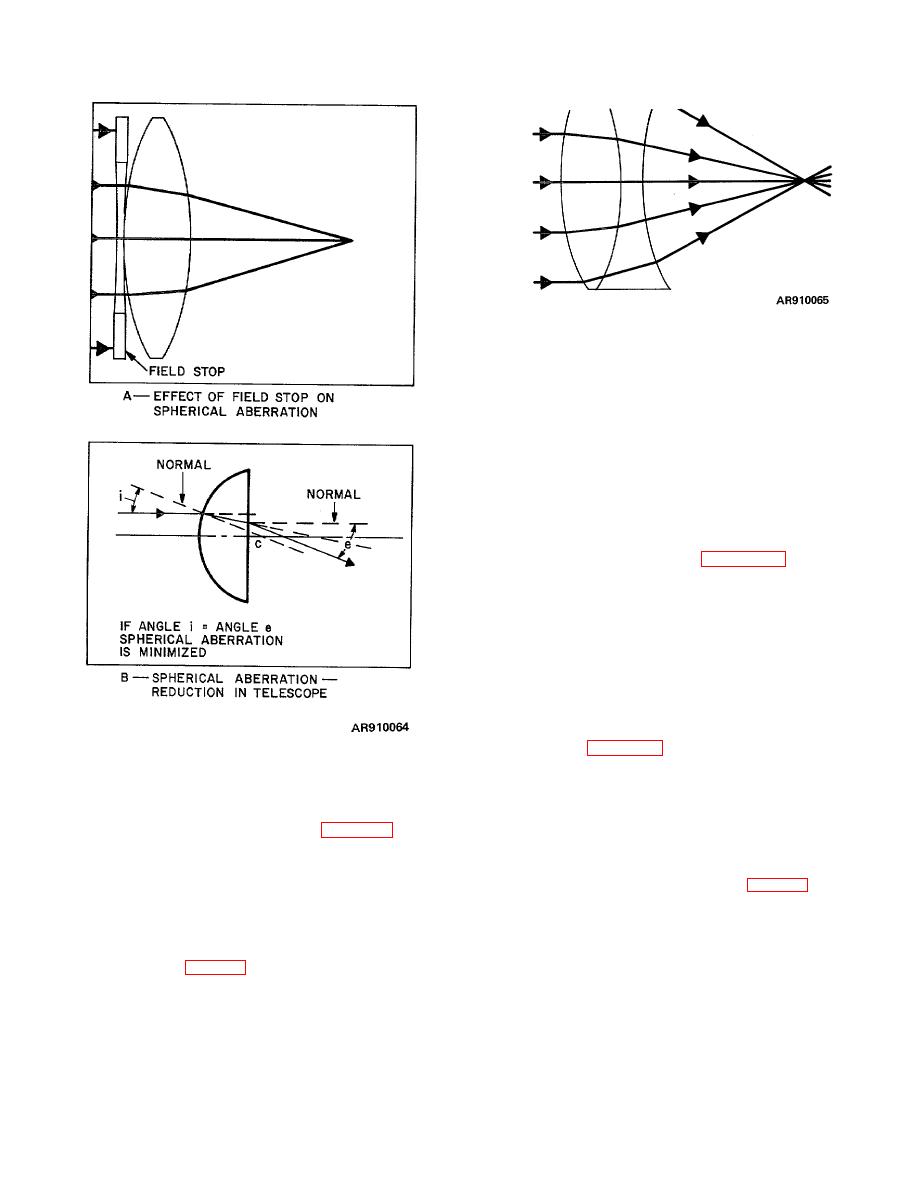
Figure 2-58. Spherical aberration reduced . |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 9-258
Figure 2-59. Effect of compound lens on spherical
aberration .
g. Spherical aberration is minimized by "bending"
the lens. Bending is accomplished by increasing the
curvature of one surface and decreasing that of the
other. This tends to eliminate spherical aberration while
retaining the same focal length. In telescope design, it is
common practice to minimize spherical aberration in yet
another way by placing the greater curvature of each
lens toward the parallel rays so the deviation at each
surface is nearly equal as in B, figure 2-58. The angles
of incidence and emergence must be equal for minimum
spherical aberration. In accord with this rule, telescope
objectives always are assembled with greater curvature
(the crown side) facing forward.
2-39.
Chromatic (Color) Aberration.
a. White light consists of all colors. Upon being
refracted through a prism, white light is dispersed into
rays of different wavelengths forming a spectrum of
Figure 2-58. Spherical aberration reduced .
various colors (para 2-27). The rays of different colors
are refracted to different extents; red undergoing the
f. In fire-control instruments, spherical aberration is
least refraction and violet the most. Inasmuch as a lens
commonly eliminated by the use of a convergent and a
may be thought of as being composed of an infinite
divergent lens cemented together to form a single
number of prisms, this dispersion also exists where light
element known as a compound lens (para 4-2). The
is refracted through a lens. This produces an optical
compound lens approximately corrects spherical
defect, present in every uncorrected single lens, known
aberration because the concave curves of the divergent
as chromatic aberration or chromatism. The violet rays
lens neutralize the positive aberration of the convex
focus nearer the lens than the red rays (fig 2-60) and the
curves. The refractive power of the combination is
rays of the other colors focus at intermediate points.
retained by the proper choice of indices of refraction for
Thus, such a lens would have a different focal length for
each of the two lenses. A lens in which spherical and
each color and the image would be fringed with
other aberrations have been minimized or eliminated is
2-44
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |