 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
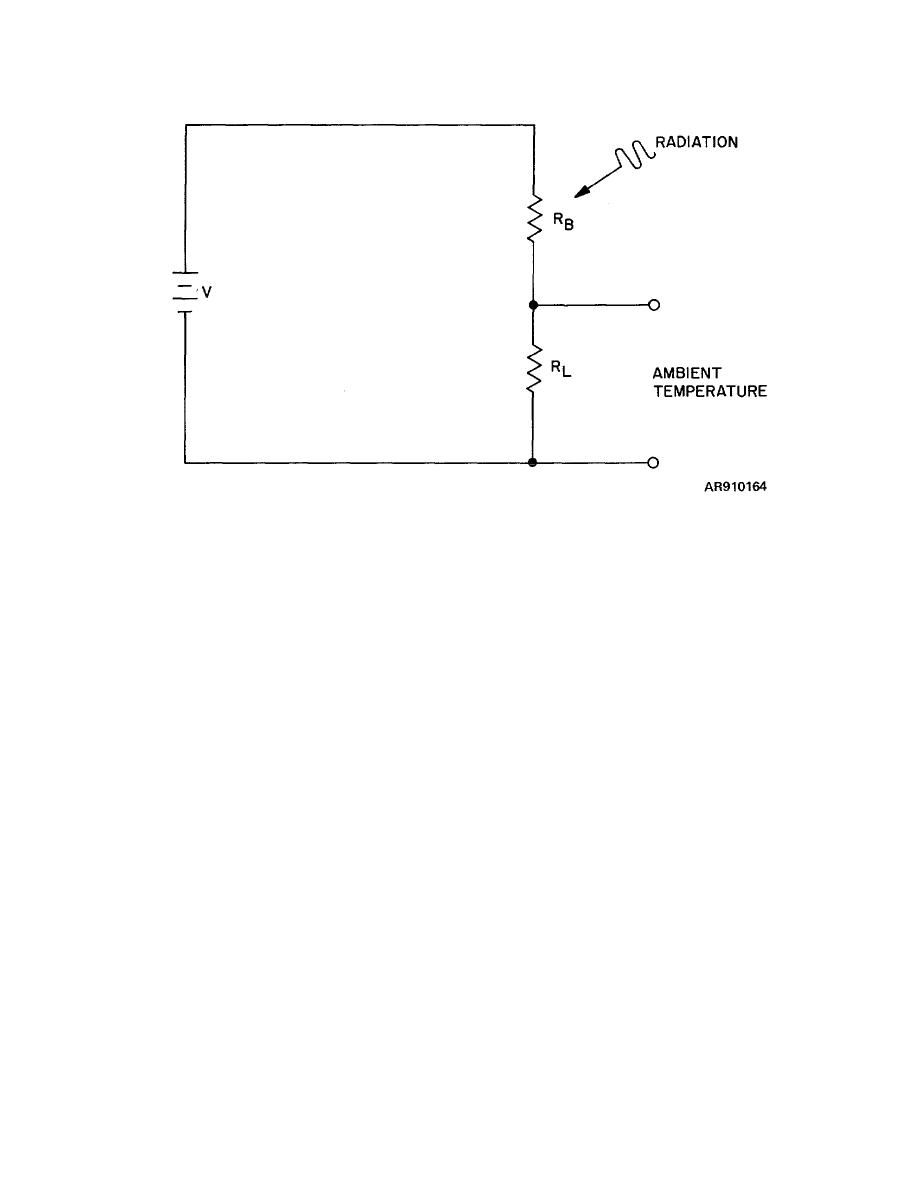 TM 9-258
Figure 7-2. Bolometer circuit.
g. Bolometers may be of three types: metal,
associated with low temperature operation and precise
temperature control are severe.
semiconductor, and superconductor.
Metal and
h. The radiation thermocouple was one of the
semiconductor bolometers are operated at ambient
temperatures, whereas the superconducting bolometer
dissimilar metals.
Absorbed radiation causes the
must be cooled to temperatures near absolute zero. A
junction temperature to rise, and the heating of the
form of metal bolometer used in microwave work
junction generates a small flow of electric current. This
consisting of an encapsulated platinum wire is known as
action is responsible for generating a voltage which is
a barretter; semiconductor bolometers are known as
proportional to the temperature rise and, therefore, is
thermistor bolometers, thermistor denoting thermally
proportional to the intensity of the radiation. A widely
sensitive resistors. Unlike a barretter the resistance of a
used form of the thermocouple is the radiation
thermistor drops as its temperature rises.
This
thermopile; it consists of a parrellel array of
characteristic has caused semiconductors to be much
thermocouples. The thermopile has a higher response
more widely used than metals from bolometers. A
than the thermocouple because of the use of multiple
superconducting bolometer has the advantage over
junctions. However, its response time is long and it is not
thermistor and metal bolometers of reduced thermal
suitable for ac amplification techniques. The fragile
noise, reduced heat capacity, and a step resistance-
construction makes it of little use in applications where it
temperature curve. On the other hand, the problems
would be subject to vibration and shock.
7-3
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |