 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Magnification by Convergent Lens |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 9-258
(2) Magnification by reading glass. If the object
formed in this way is real.
is inside one focal length of a convergent lens, the image
will be on the same side of the lens as the object
d. Object Location and Image Size. The image of
magnified, normal, and erect. The image will no longer
an object located at any distance beyond two focal
be real but will be virtual. This is a condition which can
lengths of the lens is smaller than the object. If the
be illustrated easily by the use of a reading glass (figs 2-
object is at two focal lengths, the image is the same size.
48 and 2-69). Eyepieces of all optical instruments
If the object is between one and two focal lengths away,
provide the eye with a virtual image. If the observer
the image is magnified. All of these images are inverted,
looks at the object, for example, a portion of a printed
reverted, and real. If the object is at one focal length, the
page, through a reading glass held close to the type, the
rays are parallel after refraction; the image is said to be
printed letters appear larger than they actually are. As
at infinity.
he moves the glass away from the type, each letter
appears larger and remains clear provided he moves his
e. Magnification by Convergent Lens.
eye backward as he moves the glass away from the
(1) Conjugate foci. These are two points so
printed page. At a certain point the printed letters appear
related that an object at either point will be imaged by a
at their largest and clearest. Beyond this point they
lens at the other point and will be a real image. The
become blurred and then inverted. The time when the
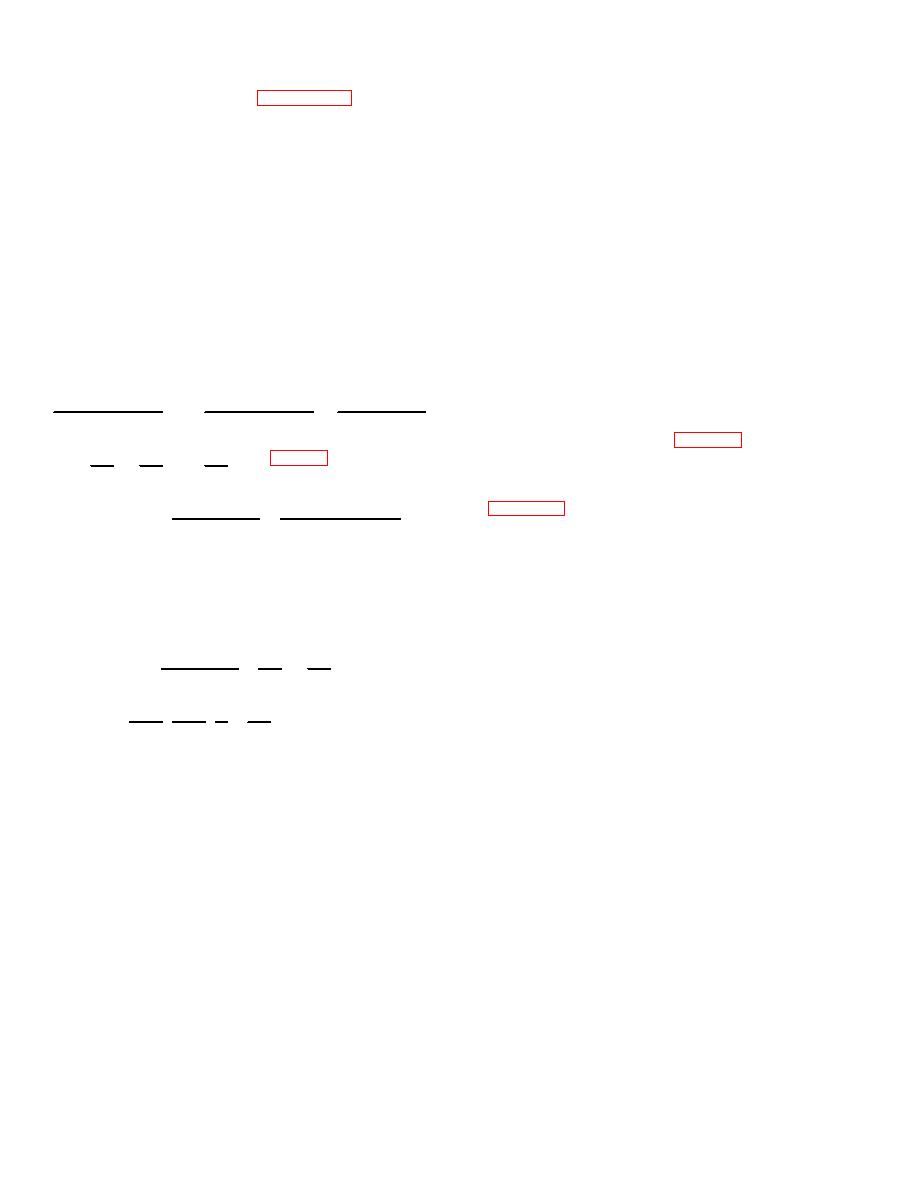
mathematical relationship is as follows
largest and clearest view of the letters is obtained is just
before the focal point of the lens has been reached. The
1
plus
1
1
rays from the object can be plotted for any point in the
Object Distance
Image Distance Focal Length
preceding demonstration (fig 2-48). A ray of light
through the center of the lens passes through in a
or
1
1
1
straight line unchanged. A ray which is originally parallel
f
0d
Id
to the axis is directed towards the point of principal focus
Magnification = Size of Image = Image Distance
image is clear considering that the virtual (not real)
Size of Object Object Distance
image is located where the emergent rays would
intersect if they were extended backward as imaginary
If any three of the above quantities are known, it is
lines. These rays form a magnified image of the object
possible to determine the fourth by the application of
which appears to be in back of the object.
simple algebra. To state magnification another way, it is
simply comparing the size of the image with the size of
the object or:
Magnification= Image Size
Y1
= Id
or
Object Size
Y
Od
1
M = Y1=f
f=x
Y
Y Od-f
x
f
2-34
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |