 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Figure 6-5. APE 1236 deactivation furnace (discharge assembly) |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
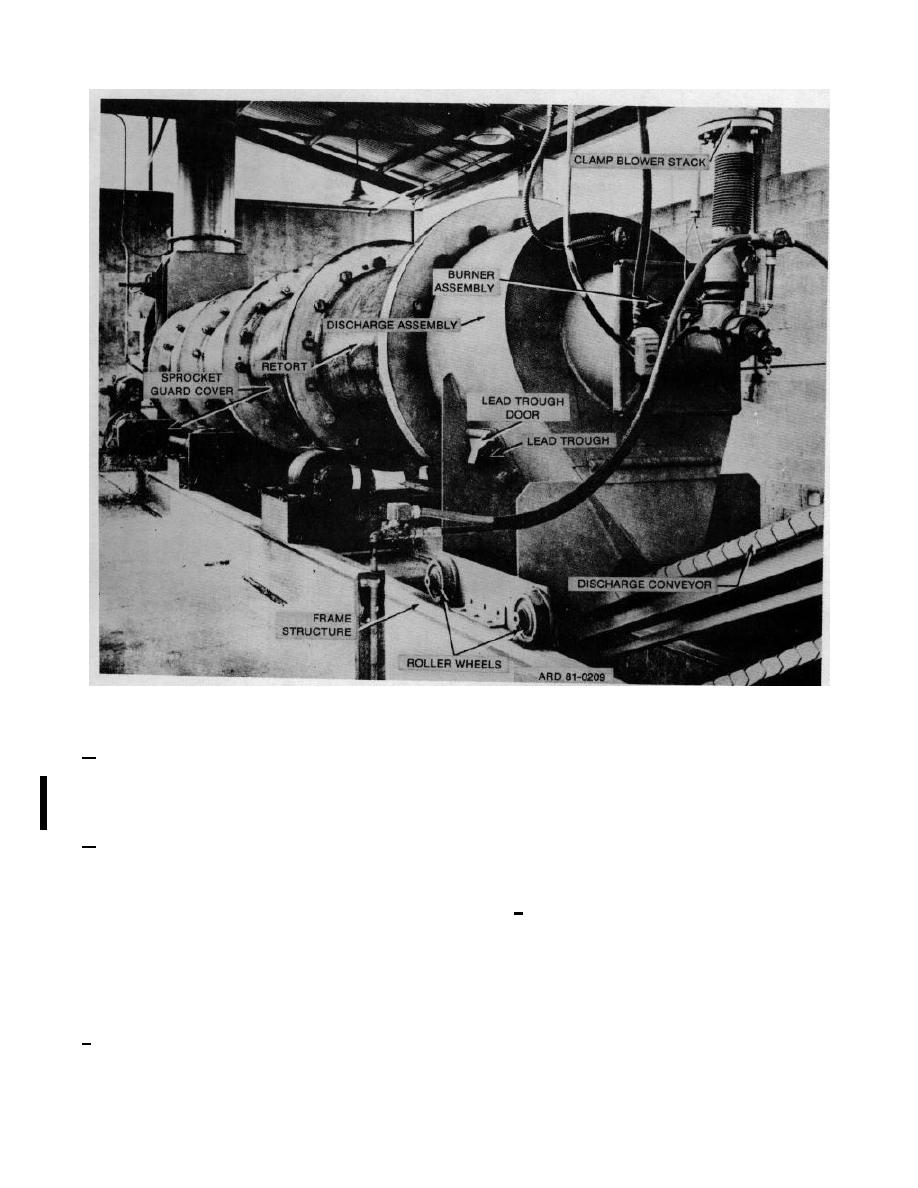 TM 9-1300-277
Figure 6-5. APE 1236 deactivation furnace (discharge assembly).
These grounds provide the capability for open burning of
g. The APE 1236 Deactivation Furnace is
scrap propellants and explosives, wooden and fiber
described in detail in the Army "Operation and
boxes, fiber containers, and other unserviceable
Maintenance Manual, Deactivation Furnace APE 1236,"
combustible materials common to ammunition
9 December 1970, U.S. Army Armament, Munitions
operations. The burning process is accomplished by
and Chemical Command, Dover, New Jersey.
burning unserviceable combustibles which in turn ignite
h. Naval Sea Systems Command Publication TK
scrap propellants and explosives. This process is also
3P90R01, April 1980, provides data for processing
used to flash off residue explosive from large metal
munitions through the Rotary Deactivation Furnace
components.
(APE 1236). The publication provides the explosive
b. Other than the now-banned ocean dumping,
weight, propellant weight, unit weight, temperature
open burning is perhaps the oldest and most universal
setting, RPM, and feed rate for various munitions by
demilitarization technique. Unwanted material is piled in
NSN. This publication provides an excellent guide for
a remote, open field with sufficient starter fuel such as
types of munitions which can be processed through the
wastepaper, scrap dunnage, etc., and ignited. There is
furnace.
no elaborate equipment, negligible fuel cost, and little
6-8. OPEN BURNING GROUNDS
labor required. However, it
a. Open burning grounds provide
a
very
economical means of demilitarization.
Change 2 6-9
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |