 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Figure B-8. Centers of curvature |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 9-258
Case I pointing (or firing) - Direct pointing, laying, or
Blind spot - The part of retina, inner coat of eyeball,
not sensitive to light where the optic nerve enters.
fire; gun pointing in which direction and elevation are set
Bore sight - A sighting device consisting of a breech
with sight of telescope pointed at the target.
Case II pointing (or firing) - Combined direct and
element and a muzzle element which, inserted in a gun,
indirect pointing, laying, or fire; gun pointing in which
is used to determine the axis of the bore and the
direction is set with a sight or telescope pointed at the
alinement of other sighting equipment with the axis of the
target and the elevation with an elevation quadrant,
bore. A bore sight may consist of a metal disk with a
range quadrant, or range disk.
peephole for the breech and a pair of crosslines for the
Case III pointing (or firing) - Indirect pointing, laying,
muzzle (fig B-6).
Boresight - To adjust the line of sight of the sighting
or fire; gun pointing in which direction is set with an
instrument of a gun to the axis of the bore (fig B-6).
azimuth circle or with a sight or telescope pointed at an
Brightness of image - A term used to denote the
aiming point other than the target; the elevation is set
with an elevation quadrant, range quadrant, or range
amount of light transmitted by an optical system to give
disk.
definition to the image seen by the observer.
Cataract - A diseased condition of the human eye in
Burnishing - The process of turning a thin edge of
which the cornea or crystalline lens becomes opaque
metal over the edge of a lens to hold it in place in its cell
resulting in blindness.
Cell - A tubular mounting used to hold a lens in its
Burnished optics are usually procured as assemblies,
proper position. The lens may be held in the cell by
inasmuch as it is difficult to replace their component
burnishing or by a retaining ring.
parts.
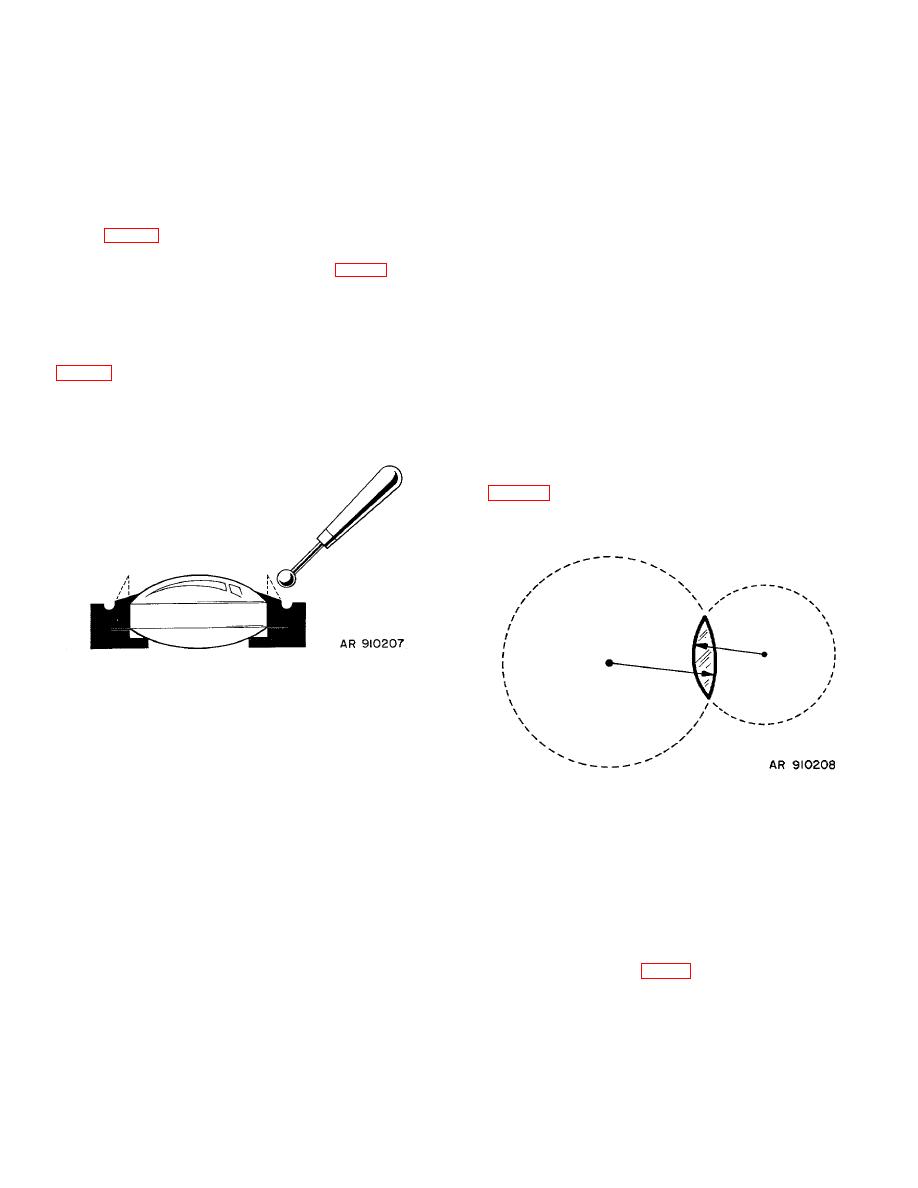
Center of curvature - The center of the sphere of
which the surface of a lens or mirror forms a part. Each
curved surface of a lens has a center of curvature
concave.
Figure B-7. Burnishing
Figure B-8. Centers of curvature
Centric Pencil - Oblique pencil or cone of light which
Calcite - See Iceland spar.
Canada balsam - A clear, practically colorless sap
passes through the center of a lens at a considerable
angle to the principal axis.
of fir, solidifying to a transparent resin used in cementing
Choroid - The opaque middle coat or tunic of the
optical elements together particularly the components of
human eye. It is a deep purple layer made up of blood
a compound lens.
It is used because it has
vessels; it supplies nourishment to the eye tissues and
approximately the same index of refraction as glass.
Candlepower - A unit of measure of the brightness
shuts out external light (fig 3-2).
Chromatic aberration - An aberration (deviation from
or power of any light source. One candlepower is the
normal) of a lens which causes
rate at which a standard candle, initially made of sperm
whale oil, 7/8 inch in diameter, burning at the rate of 120
grains per hour, emits light. Current standards of
candlepower are electric lamps.
B-7
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |