 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
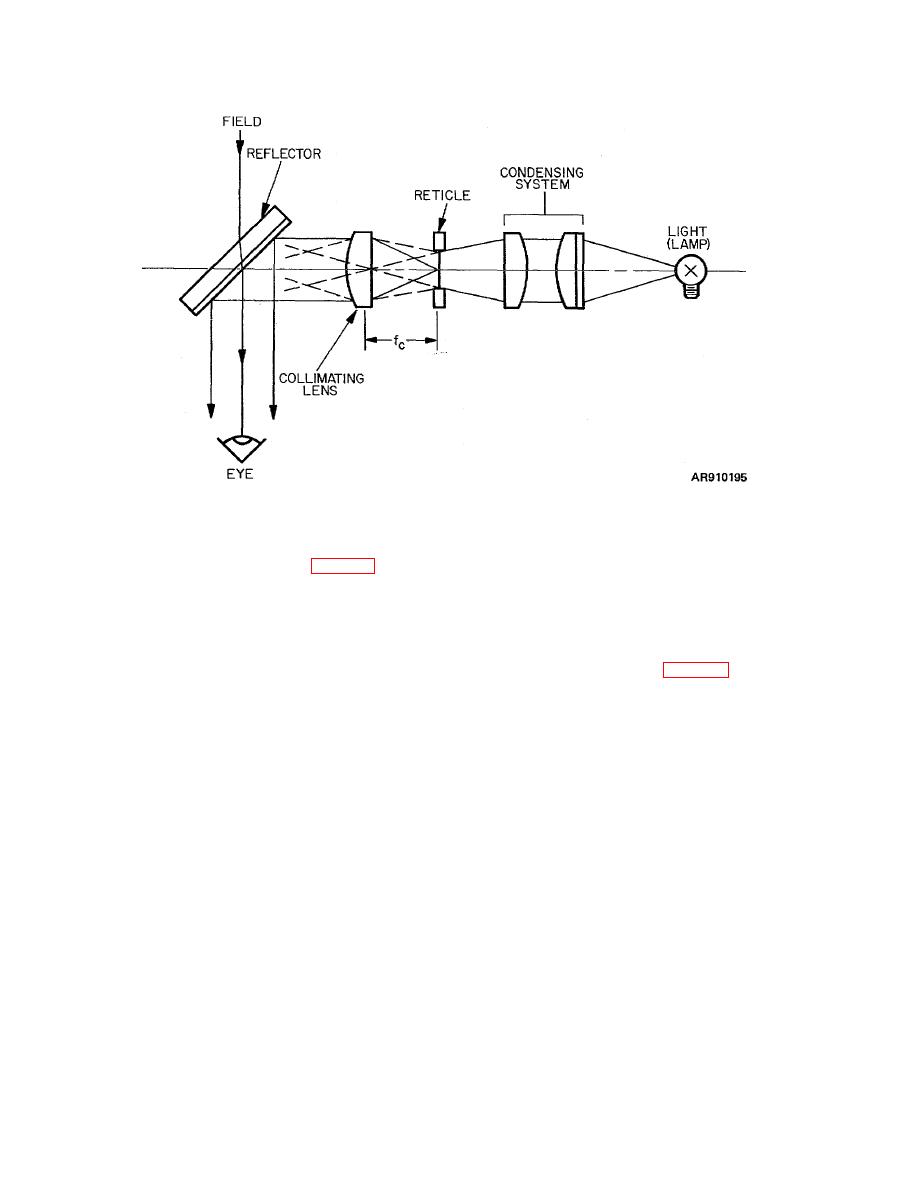 TM 9-258
Figure 8-28. Reflex sight.
a. Condensing Lens. Light from a lamp or reflected
the image of the reticle are parallel, due to the action of
sunlight is concentrated on the reticle (para 4-9), usually
the collimating lens, the reticle pattern appears at infinity
by using a condensing lens or lens system. A frosted
which makes it possible for the observer to super-impose
surface (either one surface of the condensing lens or of
the image on the target and focus on both at once.
a plane glass plate) may be used to diffuse this light and
e. Use.
The reflex sight is a projection-type
obtain even illumination of the reticle. This light then
collimator sight used for direct sighting of machine guns.
passes through either a perforated reticle (usually
8-26. Aiming Circle.
punched in a metal disk) or illuminates a reticle pattern
a. The aiming circle (fig 8-29) is used to measure
etched on glass.
the azimuth and elevation bearing angles of a ground or
b. Collimating Lens. Light from the illuminated
aerial target with respect to a preselected base line. The
reticle passes through a collimating lens placed one focal
aiming circle has many of the characteristics of a
length from the reticle. The collimated light from the
surveyor's transit. Basically, it consists of a telescope
reticle is ordinarily introduced into the field of view by the
mounted on a mechanism which permits unlimited
use of a high-reflectance-coated glass plate which
azimuth and limited elevation movements. By rotating
permits light to pass straight through from one side but
two orientating knobs, zero azimuth heading with respect
reflects most of the light coming from the opposite
to magnetic north or any other selected compass
direction. A half-silvered mirror may perform the same
heading can be established. The azimuth orienting
function but less efficiently.
control knobs can be disengaged for rapid movement by
c. Parallax. To remove parallax from this type of
exerting an outward pressure on the knobs.
The
optical system, either the collimating lens or the reticle
mechanisms are spring-loaded and will reengage when
must be moved until the reticle pattern .s clearly defined
outward pressure is removed. A locking device secures
or sharply focused when viewed through the collimating
the compass after the orienting adjustment, has been
telescope.
made.
d. Operation. Since the reflected light rays from
8-28
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |